When surfing the Internet, have you ever wondered why certain websites have a different website address, like blog.example.com instead of simply example.com? That is a subdomain in action. Now, precisely what is a subdomain?
Simply put, a subdomain is an extension of your main domain, referring to a separate “department” in your website’s “building”. This article will guide you through everything you need to know about subdomains: what they are, what they gain access to, and how to create a subdomain for your website. Now, shall we move forward?
1. What is a subdomain?

A subdomain may also be referred to as a child domain, an extension of the main domain coming just before the root domain and separated from the root domain by a dot. Consider the house your site; the subdomains are the rooms where various activities occur. A primary domain like example.com would have subdomains like blog.example.com, shop.example.com, or support.example.com.
Subdomains allow for the subdivision of a larger running site into zones that focus on specific tasks. Subdomains are used for various things, and you’ve likely encountered them daily without realizing it. Some typical examples include blogs often using blog.example.com to separate blog content from their main website and online stores using shop.example.com for their store.

Additionally, support pages frequently use support.example.com. Various language versions of a website may use subdomains like es.example.com for Spanish or m.example.com for mobile versions. Popular websites like WordPress and Shopify also employ subdomains to build different areas that allow users to navigate and use various features easily.
2. How do subdomains work?
A subdomain is not completely independent but relies on the Domain Name System. Once you enter, for any subdomain, an address such as blog.example.com in your browser, the DNS will first try to search for the records on that subdomain from the DNS records of its parent domain, example.com. Rediscovering such records returns the server’s IP address that hosts blog content for the subdomain.

A subdomain is typically linked to a specific folder or subdirectory on the server. For instance, the blog.example.com subdomain might correspond to the /blog folder on your server. Once the browser locates the correct IP address and folder, it retrieves the subdomain’s content from that location. DNS and directory mapping work together to ensure that when you access a subdomain, you arrive at the right place where its content is stored.
3. What are subdomains used for?
Subdomains are versatile tools for various purposes, helping optimize your website’s structure and user experience. One of the most common applications is creating separate blog pages. Using a subdomain like blog.example.com, you can separate blog content from your main website, making it easier to manage and improve your users’ reading experience. Subdomains are also utilized to handle various language versions of a website. For instance, fr.example.com can serve as the French version.

Furthermore, subdomains are also very helpful in categorizing and separating product or service sections. For example, an online store might use store.example.com to display products and separate them from the company’s information website. Thanks to these applications, subdomains help organize websites in a clearer, more professional, and more effective way.
4. Subdomain structure and syntax
Subdomains are structured very simply, consisting of two main components: a prefix and a main domain. The prefix is the part before the main domain, separated by a dot. For example, in the address blog.example.com, the blog is the prefix, and example.com is the main domain.

The prefix can be any word or phrase you want, depending on the intended use of the subdomain. Some other visual examples include shop.example.com, support.example.com, or news.example.com. You can see that subdomains always follow the rule: [prefix].[main domain]. This helps create an easy-to-understand and easy-to-manage structure for your website.
5. Relationship to the main domain
Subdomains and primary domains are interconnected yet distinct. The primary domain can be equated to a house or a building, while subdomains are various departments or areas in that house or building. Subdomains depend on the primary domain, meaning they cannot exist independently.

For example, blog.example.com is linked to the main domain example.com. Although subdomains have content and functions, they share resources and authority from the main domain. However, subdomains still operate relatively independently and can be optimized for SEO separately. This provides flexibility in managing and developing your website.
6. How many subdomains can a domain have?
Subdomains of a normal domain: In general terms, the technical answer is that there is no hard limit to the number of subdomains that a domain may have; factually speaking, many things should be considered, taking into account the intention of running and technical issues. Domain Name System (DNS) management systems usually allow for creating many subdomains, but creating too many can make it difficult to manage and optimize your website.

As a recommendation, you should create enough subdomains to avoid overuse to not negatively affect your website’s performance and SEO rankings. Large websites, like e-commerce sites or platforms that provide different services, might use dozens or hundreds of subdomains to serve specific purposes. However, a few subdomains are sufficient for most websites to meet your needs.
7. Why use subdomains?
You should implement subdomains on your site for many reasons. Most importantly, subdomains allow you to organize the site more clearly. Different types of content can be divided into a blog blog.example.com, online shop shop.example.com, or a support forum (support.example.com), which improves UX and website navigation.

Secondly, subdomains can enhance branding and targeted marketing efforts. For instance, you could create a dedicated space for university students at students.example.com. Subdomains have various SEO advantages, as you can optimize them for specific keywords and thus leverage higher search engine rankings. However, you should note that search engines may treat each subdomain as its own website, so having good SEO for each subdomain is important.
8. How to create a subdomain: A step-by-step guide
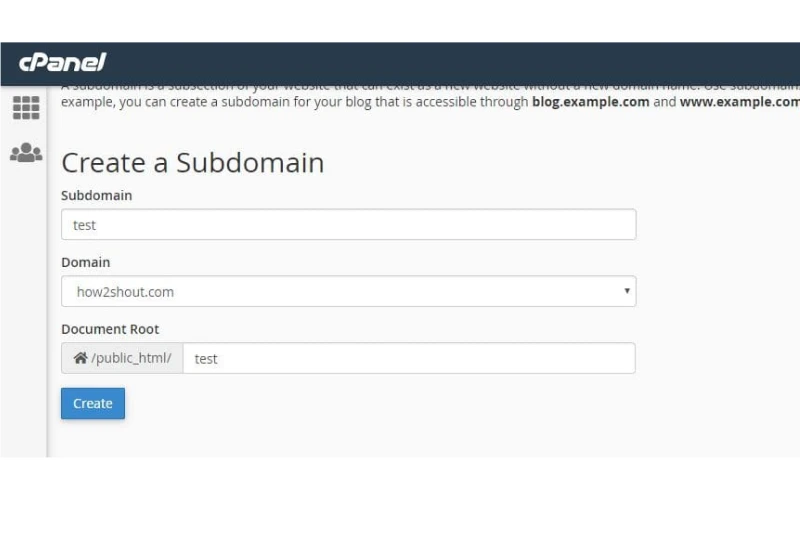
To create a subdomain for your website, you can follow these steps:
1. Get into your domain registrar or the hosting control panel (like cPanel or DirectAdmin).
2. Look for the DNS settings or subdomain management section. It usually has a name like DNS Settings, Subdomain Management, or DNS Zone Editor.
3. Enter the subdomain prefix you want to use (for example, blog, shop, or support).
4. Then, you need to configure any necessary settings, such as specifying the folder or server where the subdomain will point to. (Creating a new folder on your hosting for this subdomain is suitable.)
5. Save your changes and wait a few minutes for the DNS to update. (The update time may vary depending on the provider). If you have a popular hosting control panel like cPanel, you can easily find more detailed instructions, often with screenshots to help you follow along.
9. Subdomains vs. Subdirectories

The content of a domain can be organized in two ways: subdomains (for example, blog.example.com) or subfolders (example.com/blog). Each has its advantages and disadvantages. We have already covered how the subdomains can be considered ‘child’ websites, whilst with subfolder websites, the primary domain contains all the folders and files.
On the other hand, search engines usually treat subdomains as separate sites but include subdirectories under one main site for SEO. You can finally determine whether to go for a subdomain or subdirectory by looking into these factors:
- SEO: Subdomains can be optimized for SEO separately, while subdirectories usually inherit SEO power from the main website.
- Organization: Subdomains are suitable for completely separating content and functionality, while subdirectories are suitable for grouping related content.
- Branding: Subdomains help create separate brand experiences for target audiences, while subdirectories tend to be consistent with the main website. The final decision depends on your website’s goals and development strategy.
10. Conclusion
So, we’ve explored what is a subdomain, from its definition and functionality to its applications and advantages. Subdomains are not just an extension of your domain, but also a powerful tool to help you organize your website, target your audience, and optimize SEO.
You can confidently create and manage your subdomains with the above-detailed guidance. Consider using subdomains to enhance user experience and take your website to the next level. Don’t hesitate to experiment and explore the power of subdomains. And remember to follow our blog for more information!
11. FAQs about subdomain
How many subdomains can I have?
Technically, you can create a lot of subdomains for one domain, but you should consider your purpose and management capabilities to achieve the best results.
Are subdomains significant for SEO?
Yes, subdomains can and do affect SEO, as search engines may often treat them like separate websites, which would entail a different SEO strategy.
What is the difference between a subdomain and a subdirectory?
A subdomain (e.g., blog.example.com) is considered a website extension and exists on its own, while sub-directories- or subfolders (e.g., example.com/blog)-are just another file folder in your main website.
Do subdomains clasp another round of subdomain?
Despite the possibility of creating subdomains of subdomains (for instance, blog.shop.example.com), this is rarely necessary and may create difficulties in management; thus, it is generally best to refrain from doing so.
How do I remove a subdomain?
To delete a subdomain, you need to go to the DNS or subdomain management section in your hosting control panel and find the option to delete or remove that subdomain.